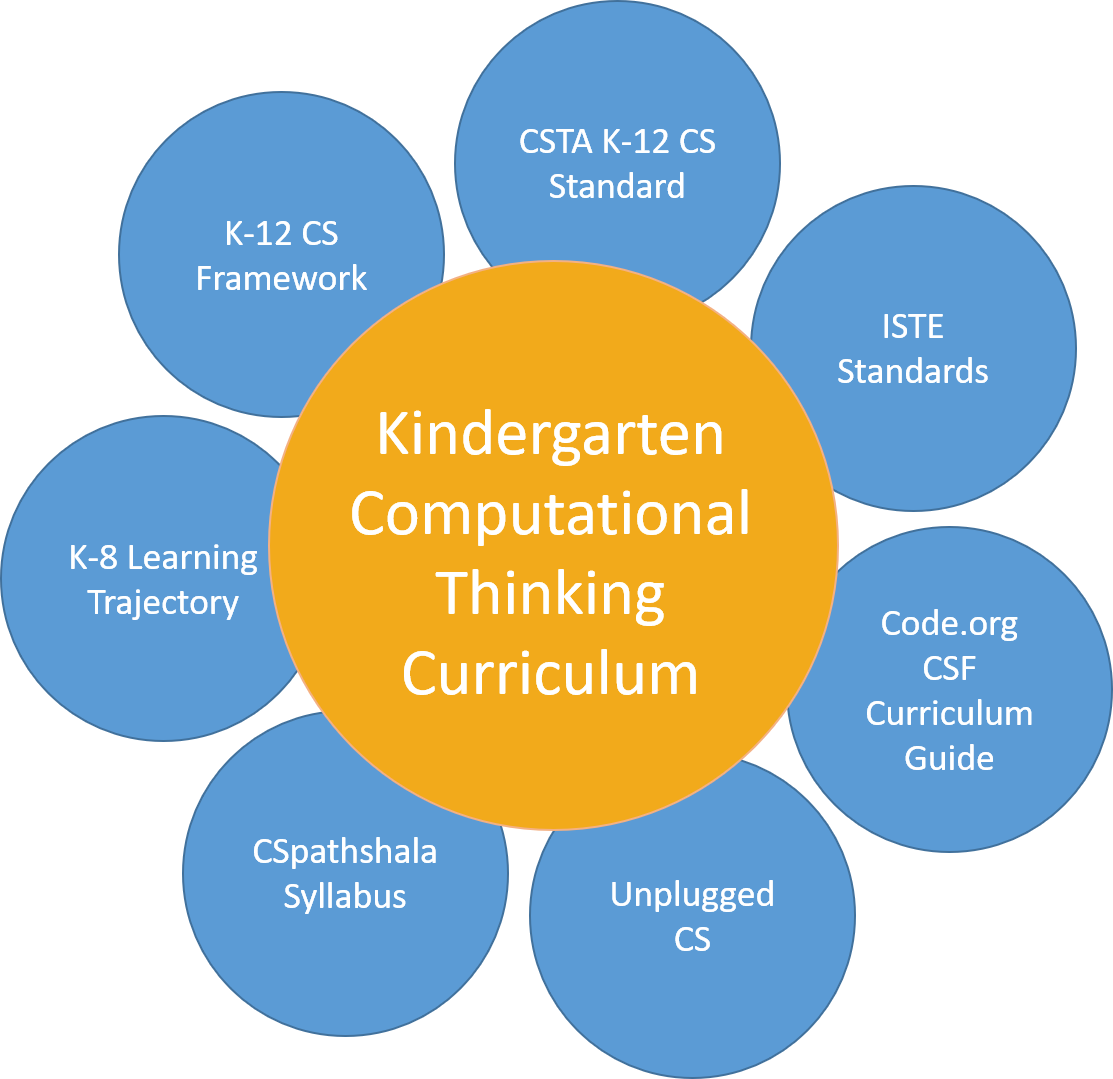
Kindergarten Computational Thinking
curriculum is aligned with international standards.
Several countries are following the standards established in the United States of America.
We follow those standards and at the same time get informed about standards from countries with deep experience in Kindergarten Computational Thinking curriculum implementation.
We also localize our lessons so that they are aligned with the standards set by education departments or ministries in regions where our Partners are located.
Kindergarten Computational Thinking Curriculum
Concept
Subconcept
Learning Objective
Algorithms &
Programming
Modularity -
Decomposition
Computing
Systems
Devices
Operate devices and recognize they have functions for specific tasks.
Algorithms &
Programming
Algorithms
Describe daily activities as algorithms.
Algorithms &
Programming
Algorithms
Describe daily activities as algorithms.
Impacts of
Computing
Social
Interactions
Demonstrate how to work respectfully and responsibly with others.
Algorithms &
Programming
Control -
Sequence
Understand that instructions need to be precise to achieve the intended outcome.
Algorithms &
Programming
Program
Development
Give attribution to ideas and creations of others while developing programs.
Algorithms &
Programming
Control -
Sequence
Understand that instructions need to be precise to achieve the intended outcome.
Algorithms &
Programming
Control -
Sequence
Understand that instructions need to be precise to achieve the intended outcome.
Networks &
the Internet
Cybersecurity
Understand the need to protect devices and information from unauthorized access.
Impacts of
Computing
Safety, Law,
and Ethics
Demonstrate how to login and logout of devices.
Networks &
the Internet
Network
Communication
& Organization
Understand that devices communicate with each other using a communication network.
Computing
Systems
Hardware &
Software
Understand the hardware and software components of computer systems.
Algorithms &
Programming
Program
Development
- Debugging
Understand that making mistakes play a valuable role in the problem-solving process.
Algorithms &
Programming
Program
Development
- Debugging
Understand that making mistakes play a valuable role in the problem-solving process.
Algorithms &
Programming
Control -
Sequence
Understand that precision and completeness are important when writing instructions in advance.
Algorithms &
Programming
Control -
Sequence
Understand that precision and completeness are important when writing instructions in advance.
Algorithms &
Programming
Control -
Loops
Understand that some tasks or activities involve repeating actions.
Algorithms &
Programming
Modularity
Recognize that a good way to understand a problem is to break it down into smaller problems.
Algorithms &
Programming
Modularity
Recognize that a good way to understand a problem is to break it down into smaller problems.
Data &
Analysis
Storage
Understand that computers store data that can be retrieved later.
Data &
Analysis
Collection
Understand how devices and gadgets collect data.
Data &
Analysis
Visualization &
Transformation
Understand how devices and gadgets present data.
Data &
Analysis
Inference &
Models
Understand the uses of data.
Algorithms &
Programming
Control -
Loops
Understand that an instruction that uses repeat language generates the same result as an instruction repeated several times.
Algorithms &
Programming
Program
Development
Develop a plan that describes a program's goal, sequence of actions, and expected result.
Algorithms &
Programming
Control -
Sequence
Understand that precision and completeness are important when writing instructions in advance.
Algorithms &
Programming
Program
Development
- Debugging
Use the result to decide whether or not there are errors.
Algorithms &
Programming
Program
Development
Develop a plan that describes a program's goal, sequence of actions, and expected result.
Algorithms &
Programming
Program
Development
- Debugging
Use the result to decide whether or not there are errors.
Computing
Systems
Troubleshooting
Understand when devices have problems and describe them using common terminology.
Impacts of
Computing
Culture
Define how computing has positively changed how people live and work.
Algorithms &
Programing
Variables
Understand that information in the real-world can be represented in programs.
Learning Trajectory

A learning trajectory consists of a set of learning objectives, a development path to achieve the learning objectives, and activities to help students move along the development path.
We reviewed the grade-band learning objectives established by International Standards and determined the grade-level learning objectives. Then we distributed the grade-level learning objectives throughout the school calendar. Lastly, we established the learning trajectories.
We also thought of age-appropriate learning and assessment tools to help students navigate through the learning trajectories.
The learning trajectories, as well as the learning and assessment tools, are embedded in the Kindergarten Computational Thinking curriculum.
Learning Trajectories
Computing Systems
Operate devices and recognize they have functions for specific tasks.
Understand the hardware and software components of computer systems.
Understand when devices have problems and describe them using common terminology.
Networks & the Internet
Understand the need to protect devices and information from unauthorized access.
Understand that devices communicate with each other using a communication network.
Data & Analysis
Understand how devices and gadgets collect data.
Understand that computers store data that can be retrieved later.
Understand how devices and gadgets present data.
Understand the uses of data.
Algorithms & Programming
Understand that systems are made up of parts.
Describe daily activities as algorithms.
Understand that instructions need to be precise to achieve the intended outcome.
Give attribution to ideas and creations of others while developing programs.
Understand that making mistakes play a valuable role in the problem-solving process.
Understand that precision and completeness are important when writing instructions in advance.
Understand that some tasks or activities involve repeating actions.
Recognize that a good way to understand a problem is to break it down into smaller problems.
Understand that an instruction that uses repeat language ("Go up 3 times") generates the same result as an instruction repeated several times ("Go up, go up, go up.").
Develop a plan that describes a program's goal, sequence of actions, and expected result.
Use the result to decide whether or not there are errors.
Understand that information in the real world can be represented in programs.
Impacts of Computing
Demonstrate how to work respectfully and responsibly with others.
Demonstrate how to login and logout of devices.
Define how computing has positively changed how people live and work.
Do you want to know more about how to implement the
Kindergarten Computational Thinking curriculum in your community?